Last Quarter 2019, the global economy seemed to be on the way to recovery, financial markets seemed bullish, growth projections were positive and trade and political tensions were somewhat “subdued”. Now all bets are off. As COVID-19 spreads around the globe, it has become clear that it has the potential to derail the world economy.


Health Pandemic and Its Measured Impacts
MORTALITY
The 21st century has witnessed several pandemic outbreaks: Avian Flu, Swine Flu, Mers, SARS, etc only the 2002–2003 SARS outbreak seems truly comparable.
So far, the novel coronavirus appears:
- Less deadly to those infected: with an estimated mortality rate of 2%-3% vs SARS’ rate of 6.6%
- More Contagious: 8x more cases and deaths.

FINANCIAL TERMS – GLOBAL
The economic effect of this pandemic is different from similar pandemics. The hardest-hit countries make up a majority of the top 10 economies in the world, accounting for 60% of global GDP, 65% of global manufacturing, 40% of global manufacturing exports.
While a short-and-sharp crisis is still possible, it’s looking less like the most likely outcome. Recent containment approaches are hindering global production and productivity, leading to macroeconomic drops in aggregate demand and delays in purchase and investments by consumers and firms.
The below snapshot shows the forecasted global costs of covid-19 compared to the cost of 2003 SARS pandemic

FINANCIAL TERMS – CHINA
In 2003 China’s economy which represented ~4% of global GDP was only RMB 13.74 trillion and SARS reduced her GDP by almost 1% or approximately 100billion
With an economy size of almost RMB 100 trillion today, China’s economy is 50x larger than it was in 1980 and 7x larger than 2003 and makes up about 16% of global GDP
Current estimates of coronavirus’s economic impact call for a 0.2%–0.5% reduction in China’s GDP, which could cost as much as RMB 500 billion ~$71million

Forecasted Impact on Sectors and Industries
FINANCIAL MARKETS
- There will be gainers and losers ($5 trillion was wiped from global financial markets as at end of 6th March 2020).
- As of Feb end, stock markets had fallen by 8% in America, 7.4% in Europe & 6.2% in Asia.
- Widespread country Interest rate cuts (US, China, Canada, Thailand). Greater negative impact in sectors such as consumer discretionary and gains in health care.
SUPPLY CHAIN
- Considering China is the world 2nd largest economy aka the “worlds factory”
- Companies sourcing from china experience a halt in production activities
- At least 51,000 companies worldwide, 163 of which are in the Fortune 1000, have one or more direct or “tier 1” suppliers in the impacted region.
- A 30% drop in Baltic Dry Index and +15% in TAC index
LUXURY GOODS
- 1/3 of global spending on luxury brands comes from china
- Closures in luxury brand subsidiaries headquartered in Hong Kong resulting in a “material negative” effect on luxury demand
ENERGY: OIL AND COAL
- Worlds largest energy consumer
- Transport sectors will be affected in a major way.
- Fall in commodity prices (crude, coal, etc.)
- Reduce demand for fuel.
- Oil prices have already declined, from $68 per barrel (Brent crude) to $54 at end of February 2020 and currently $36, with most of the decline over the past two weeks. A reduction in oil demand of 20% is expected (Durden, 2020)
AUTOMOBILE
- Data from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM) has revealed that auto sales declined by 18% in January, as reported by Reuters
TOURISM
- Weaker demand for global travel
- Tourist spend spent an average of $277bn on tourism in 2018 and $300bn in 2019 forecasted to decline by over 20% in 2020
TRADE/PRODUCTION
- China share of global trade was 5% in 2003 and currently 16%
- Forecasted $50 billion drops in exports across global value chains
- The subsequent shutdown of huge swathes of China could impact more than 5 million businesses worldwide
- Chinese provinces most impacted by the virus are intricately linked to the global business network with almost half (49%) of the companies with subsidiaries in impacted regions are headquartered in Hong Kong
AVIATION
- Forecasted to take about $113billion hit
- Over 13.8% decline & change of flights bookings
- Airlines are banning flights and their stock prices are declining
- These airlines will need to offer refunds or rebook on to different flights
DIGITAL
- Spike in use of online video conferencing platforms – zoom, slack, google hangouts, etc.
- Health Care goes Digital
- Accelerated growth in online medical platforms – % increase Dec 19-Jan 20

ENTERTAINMENT AND SPORTS
Entertainment
- Global film industry forecasted to face a $5 billion loss
- Production delays/Postponements of movie releases by Disney, Sony, Warner Bros, Universal
- 6 Month – postponement of James Bond Movie which grossed $1,110,526,981 and $879,620,923 in in 2012 and 2015 respectively
- Reduction/closures of theaters, cinemas, clubs and recreational centers
Sports
- Forecasted Cancellation/Postponement of TOYKO Olympics
- Cancellation of Arctic Winter Games
- Cancellation of NBA, Football and Soccer games
Possible Economic Ramifications for Africa
Africa is much more exposed to the Chinese market than other regions around the world in terms of Trade, Infrastructure Initiatives, Investments & Exports.
China is Africa’s largest trading partner; hence the aggregated potential economic impact of reduced exports could contribute to ~$4 billion in lost revenues. Specifically:
CHINA STOPS BUYING WHAT AFRICA HAS TO SELL
- Consumer spending expected to slow down due to potential high health care costs
- The directly immediate impact on demand for Energy and African agricultural exports like cotton, Namibian beef, Rwandan coffee, Kenyan tea and South African wine and citrus
DECLINE IN AFRICAN TOURISM
- Chinese leisure and Business travel will halt hence significant downturn in passenger traffic between China and Africa
- Several African airlines have built sizeable business ferrying students, workers & tourists e.g. Ethiopian Airline, Kenya Airways,
- Significant cancellations of Festivals, Arts Exhibitions, Resort Bookings, Safari’s, etc.
GLOBAL INVESTOR FREAK OUT
- Stock exchange plunges – steady decline due to local companies’ exposures to china (JSE, Kenya, NSE)
- Pressures on African Currencies (Nigerian NGN, Kenyan KES & South Africa ZAR)
- Dumping of stocks by global investors who view Africa’s reliance on the Chinese market as a significant liability
INFRASTRUCTURE TAKES A HIT
- Slow down/halt of Infrastructural projects
- A decline in projected returns from these investments
- Longer time to repay infrastructure induced debts
- Potential reduced funding for future infrastructure projects
Potential Impact on Africa – “Nigeria”

The spread of the coronavirus virus has curbed demand in China, driving oil prices down nearly 15% this year to $36pb, significantly below the $57pb pegged by the Nigerian government in its 2020 budget. For Nigeria which depends on crude for 90% of its export revenue, this could mean a high probability for currency devaluation due to a continuous shrinkage of foreign reserves amongst others.
- Further slash in growth projection to 2% from 2.5% because of a decline in oil prices – IMF
- Negative Impact on the Nigerian Construction, Telecommunication, Oil & Gas, Automobile Industries
- Halt in Companies Operations – Manufacturers, Importers, Agro-Allied
- Borrowing Costs Expected to Rise, May affect Nigeria’s ability to Service Debts
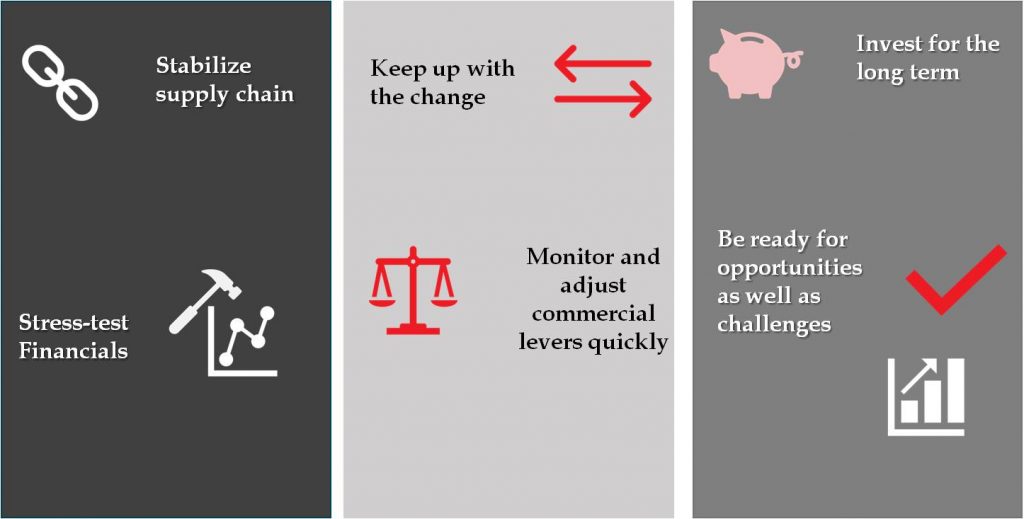
For Companies: The Time to Act Is Now
While it is too early to know for sure how severe the human and financial cost of coronavirus will be in China, around the globe particularly Nigeria, the companies that will fare best during this crisis and be best positioned during the recovery will be those that act now.